1 Introduction
This document specifies semantics and syntax constraints for rule axes. Aspect rule axes provide an implementation of predefined axes, as defined in the table specification.
2 Namespaces and namespace prefixes
Namespace prefixes [XML NAMES] will be used
for elements and attributes in
the form ns:name where ns is the
namespace prefix and name is the local name.
Throughout this specification, the mappings
from namespace prefixes to actual namespaces are consistent
with Table 1.
The prefix column in Table 1 is non normative. The namespace URI column is normative.
| Prefix | Namespace URI |
|---|---|
table
|
http://xbrl.org/2011/table
|
xbrlte
|
http://xbrl.org/2011/table/error
|
link
|
http://www.xbrl.org/2003/linkbase
|
xbrli
|
http://www.xbrl.org/2003/instance
|
xfi
|
http://www.xbrl.org/2005/function/instance
|
xbrldi
|
http://xbrl.org/2006/xbrldi
|
xbrldt
|
http://xbrl.org/2005/xbrldt
|
xl
|
http://www.xbrl.org/2003/XLink
|
xlink
|
http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink
|
xs
|
http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema
|
xsi
|
http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance
|
generic
|
http://xbrl.org/2007/generic
|
4 Definitions
The figure below provides a model of the rule axis.
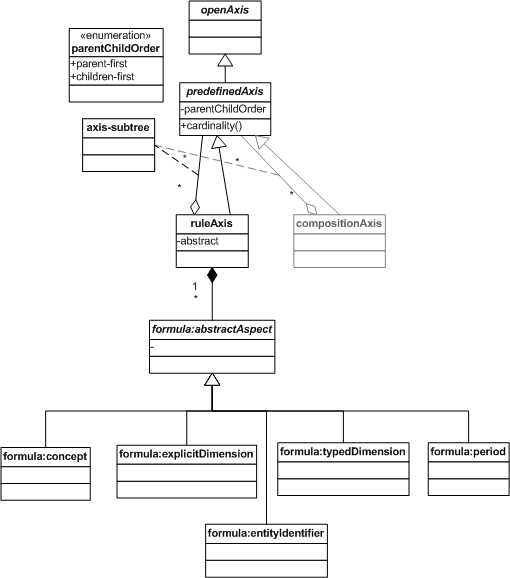
A rule axis is an implementation of a predefined axis whose set of coordinates is expressed in terms of a subtree of rule axis elements and their rules. The rule axis may have rules representing specific aspects, e.g., concept, explicitDimension, typedDimension, entityIdentifier, and period.
5 Aspect Rules
The rules of a coordinate are defined by formulae aspect rules in the corresponding axis and its subtree. In the context of the Formulae specification, aspect rules specify aspect values that the output fact is required to match. In this specification, aspect rules will be used to specify the aspect values that facts that correspond to that coordinate MUST match.
The aspect rules of a rule axis coordinate represented by a rule axis element use as source aspect values the required aspect rules of its ancestor ruleAxis elements. Where the formula specification makes reference to input instances for SAV and output instances for RAV, in this specification SAV become RAV when a source instance of existing facts is used to populate a table.
6 Headers
As described before, the headers of the axis are represented by the set of rule axis elements, their subtrees, and their rules. As axis rule element is represented using XLink resources in a generic linkbase, they can be associated to generic labels or messages, and generic references. These labels, messages, and references SHOULD be used as labels and references of the headers by a rendering engine. Labels, messages, and references are used in the normal manner of such linkbases, ignoring the link role labels and references. [Herm Fischer: Note to reviewers: please indicate if there is a use case for labels to be constrained to specific link roles, such as to match the composition of a table.]
7 Syntax
A ruleAxis is represented by a <table:ruleAxis> element with an optional subtree of <table:predefinedAxis>
elements connected by an axis-subtree relationship.
A <table:ruleAxis> element may contains <formula:aspectRule> elements used to specify
aspect and aspect constraints for the coordinate.
A <formula:aspectRule> element specifies an aspect and its value for an axis coordinate in a manner that is usable both to select input fact(s)
that match, and to use as an entry form specifying output aspects when storing values of empty cells corresponding to the coordinate aspects.
The following <formula:aspectRule> features are not processed: @source (all rules), @augment (unit rule),
and omit sub-elements (dimension rules).
The <table:ruleAxis> may have @value XPath expressions,
and the <formula:aspectRule> may have an XPath expression (such as for QNameExpression or period).
The context item for each XPath expression is the fact bound to coordinates of each axis, or the <table:selectionAxis>
result when applicable (when bound to coordinates of a cell).
XPath expressions may refer to parameters and selection axes by name, when in effect.