1 Introduction
This document specifies semantics and syntax constraints for selection axes. Selection axes provide an implementation of open axes, as defined in the table specification, based on the use of XPath expressions that select a sequence of data (not necessarily fact items), which is given a name, and usable as a variable in breakdown (nested) axes of the same axis disposition, and usable in axes expressions of the opposite axis disposition (when orthogonal to the selection axis coordinate).
(In a most general sense, if the predefinedRuleAxes and filterAxes were thought of in the same manner as fact variables for formula variable sets, the selection axes may be thought of as general variables for the table, as a simile of a variable set.)
2 Namespaces and namespace prefixes
Namespace prefixes [XML NAMES] will be used
for elements and attributes in
the form ns:name where ns is the
namespace prefix and name is the local name.
Throughout this specification, the mappings
from namespace prefixes to actual namespaces are consistent
with Table 1.
The prefix column in Table 1 is non normative. The namespace URI column is normative.
| Prefix | Namespace URI |
|---|---|
table
|
http://xbrl.org/2011/table
|
xbrlte
|
http://xbrl.org/2011/table/error
|
link
|
http://www.xbrl.org/2003/linkbase
|
xbrli
|
http://www.xbrl.org/2003/instance
|
xfi
|
http://www.xbrl.org/2005/function/instance
|
xbrldi
|
http://xbrl.org/2006/xbrldi
|
xbrldt
|
http://xbrl.org/2005/xbrldt
|
xl
|
http://www.xbrl.org/2003/XLink
|
xlink
|
http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink
|
xs
|
http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema
|
xsi
|
http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance
|
generic
|
http://xbrl.org/2007/generic
|
3 Definitions
The figure below provides a model of the selection axis.
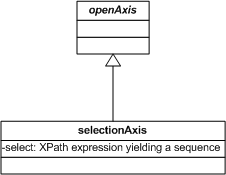
A selection axis is an implementation of open axes expressed in terms of an XPath function that yields a sequence.
Examples of selection axes fulfill these use cases:
- Extended link roles applicable to an instance (e.g., balance sheet and document information for an instance representing a balance sheet with accompanying company document information
-
Tuples in a Global Ledger instance document
- Starting balance and ending balance; or
- A selection of account codes that have transactions; or
- A set of transaction items for a selected account code.
- Contexts in an instance
- Contexts not in use in an instance
4 Coordinate ordering
The XPath selection expression produces a sequence. Although most XPath operations result in sequences that are in source instance document node order, sequences may be sorted (such as account code or name, using custom functions such as described in [XPATH SORTING]).
5 Context Item
The context item for the XPath expression of a selection may be a fact item, if the inherited axes of the selection axis, together with the coordinates of the opposite direction axisType coordinates, specify a fact item, or otherwise an empty sequence.
6 Selection
A selection yields any node of an instance or atomic data produced by an XPath expression.
If a nonabstract selectionAxis is the last coordinate for an axis, the select expression provides a way of generating renderable data from a otherwise-bound fact for a cell. For example, if the inheriting coordinates identify a fact, then the select expression may produce an aspect of the fact, such as a period end date or unit, or a footnote (or footnotes sequence), or any other data derived by table lookup.
8 Syntax
<xtable:selectionAxis> is an element with attributes @name and @select.
@name (on the axis-arc relationship) behaves like a variable name, so that the selection value can be referred to by XPath construct $name.
@coveredAspect: an enumeration type specifying what aspect is to be matched and covered. Enumeration values may be
[Hugh Wallis: This is an early list - to be updated]:
Concept: the value of the selection is a QName which matches a fact’s QName and covers the concept aspect.PeriodStart: the value of the selection is a dateTime (union) value which matches a fact’s start and covers the period aspect.PeriodInstantEnd: the value of the selection is a dateTime (union) value which matches a fact’s instant or end and covers the period aspect.PeriodInstant: the value of the selection is a dateTime (union) value which matches a fact’s instant only, and covers the period aspect..PeriodEnd: the value of the selection is a dateTime (union) value which matches a fact’s end only, and covers the period aspect..EntityIdentifier: the value of the selection is an entity identifier (token) value which matches a fact’s entity identifier and covers the entity identifier aspectUnit: the value of the selection is a QName which matches a single-measure unit and covers the unit aspect-
If instead of enumerated token, the value is a QName, it covers the QName’d dimension, and the
@matchexpression (if present) specifies a boolean match expression (where the context item is a fact being matched to the selected dimension, available as the named value of the selection.
@select is an XPath expression yielding a sequence of nodes (of instance document), atomic values
(displayable), or opaque objects (relationships from xfi: relationship functions, but must be abstract).
The following attributes are inherited from openAxis and may be used on a selectionAxis resource element:
@value: An XPath expression applied to a coordinate location (cell of table) after selection is assigned to the selectionAxis. The@valueis not assigned to the selection yielded as a coordinate value, but only available to format transform, scale, and rendering.@scale: Scaling for rendering without affecting the selection yielded@negate: Iftruespecifies that a numeric value is to be sign-flipped on rendering.@format: Format transformation applied to rendering, without affecting the selection yielded