1 Introduction
The XBRL 2.1 specification [XBRL] defines the syntax and semantics of that syntax in order to define concepts, resources and relationships between those concepts and concepts and resources in a DTS (See section 3.2 of the XBRL Specification for a more exhaustive definition of a DTS).
XBRL has been used extensively in projects around the world. A common use of the XBRL technology has been to model an existing information supply chain between regulators and regulated entities.
The digitalization of that process, using XBRL technology, has required the creation of an XBRL taxonomy (the DTS) used by people creating XBRL reports or submitting those reports to regulators.
One of the most important benefits of XBRL technology is that XBRL is a standard about how to define the report content. This means that new reporting requirements from regulators to regulated entities can usually be incorporated using the same XBRL 2.1 technology without having to change the XBRL technology. In fact, when a new version of a DTS is released, the regulated entities will have to adapt existing mappings between internal data and the old concept definitions to the new concept definitions. It is expected that for all concepts with no significant changes the mapping rules can be adapted automatically.
On the other hand, companies preparing their financial reports using the XBRL technology can create their own taxonomies or taxonomy extensions. These companies can also make changes to his own taxonomies and may have the necessity to report to the market not only the reports according to the new DTS but also the changes they made to the taxonomies. In this case, the versioning report also serves as the communication tool in order to allow them to document the changes.
Most existing XBRL APIs are able to load the content of an XBRL DTS (a taxonomy) and can generate XBRL reports according to that taxonomy. But XBRL would not provide a true benefit at all if moving the software from one taxonomy version to another (on the report production side) or the process to review two consecutive reports from a company that has made changes to their taxonomy (on the consumers side) were a costly process for the users. This specification is specifically designed to address this issue. The reporting requirements change over time, the taxonomies change to cover those new requirements, but the technology used to create reports is the same (XBRL 2.1). Moving applications to work from one taxonomy version to the next would be a trivial operation at least for concepts whose definition is the same.
1.1 Background
A number of projects have made significant contributions to this specification. These include the IASC Foundation which has contributed a methodology on which this specification is based, and the National Taxonomy Project ("NTP") initiated by the Dutch government, which has contributed the first initial documentation of a standardisation for a Versioning report. Several other initiatives such as the Committee of European Banking Supervisors have joined efforts together in order to help the XBRL Consortium and the XBRL industry to adopt a single common solution that satisfies the most critical business requirements in all those projects.
1.2 Relationship to other work
This document pertains to XBRL as defined in the XBRL Specification [XBRL].
Parts of this document may reiterate for expository clarity certain semantic restrictions imposed by XBRL, but this document does not modify XBRL. In the event of any conflicts between this document and XBRL, XBRL prevails.
1.3 Terminology
Terminology used in XBRL frequently overlaps with terminology from other fields.
The following terms are used as described in the table below:
|
Term |
Meaning |
|
Arc, arcroleRef, base set, child, concept, context, duplicate item, descendant, DTS (discoverable taxonomy set), element, entity, fact, instance, item, linkbase, linkbaseRef, p‑equal, roleRef, taxonomy, taxonomy schema, u‑equal, XBRL instance. |
As defined by XBRL [XBRL]. |
|
Relationship |
An arc defines a relationship between its source concepts and target concepts that is determined by its xlink:arcrole and other attributes. |
|
source [concept(s)] |
The concepts identified by the URI content of the href attributes of the locator-type elements in the same extended-type link element, which have the same label attribute content as the content of the “from” attribute of an arc. |
|
target [concept(s)] |
The concepts identified by the URI content of the href attributes of the locator-type elements in the same extended-type link element, which have the same label attribute content as the content of the “to” attribute of an arc. |
|
must, must not, required, shall, shall
not, should, should not, may, optional |
See [RFC2119] for definitions of these and other terms. These include, in particular: should: Conforming documents and applications are encouraged to behave as described. must: Conformant documents and consuming applications are required to behave as described; otherwise they are in error. |
|
XBRL |
Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) 2.1 Recommendation [XBRL]. |
|
From DTS |
The term "From DTS" is used to refer to the source DTS that is the DTS that will be compared to the "To DTS". The From DTS normally refers to the old taxonomy version. |
|
To DTS |
The term "To DTS" is used to refer to the target DTS or the DTS that is being compared with the "From DTS". The To DTS normally refers to the new taxonomy version. |
|
Action |
This specification uses the term "Action" for referring to what changes between the From DTS and the To DTS |
|
Assignment |
This specification uses the term "Assignment" for referring to the business reasons for an action to change things in a DTS or even the business reasons for starting to compare two DTSs. |
1.4 Document conventions
The following highlighting is used to present normative technical material in this document:
|
|
The following formatting is used for non-normative examples in this document:
The following formatting is used for non-normative counterexamples (examples of poor, discouraged or disallowed usage) in this document:
Non-normative editorial comments are denoted as follows and removed from final recommendations:
1.5 Namespaces
This table contains all the prefixes used within the text and XPath 2.0 expressions and the correspondent namespace URI:
|
Prefix |
Namespace URI |
|
xml |
http://www.w3.org/XML/1998/namespace |
|
xbrli |
|
|
xs |
|
|
xlink |
|
|
link |
|
|
xl |
|
|
Error! Reference source not found. |
Error! Reference source not found. |
The Prefix column in the table above is non normative. The Namespace URI column is normative.
1.6 XPath
XPath expressions that appear in this document are XPath 2.0 [XPATH] expressions executed in a schema aware processor. Refer to the [XPATH] 2.0 specification for more information.
The prefixes used in the XPath expressions are indicated in section 1.5 above.
2 XBRL Versioning
Versioning is a term with several meanings. Different people have different interpretations of this term. XBRL Versioning is about standardising the content of a report of "information about the changes made to a taxonomy" in order for taxonomy users to save time in adapting their applications to a new taxonomy version.
This specification distinguishes between “technical differences” and “semantic differences”. “Technical differences” are those that can be automatically identified by software comparing the properties of the pair of information items under observation. “Semantic differences” are the interpretation of the “technical differences” made by the author of the versioning report. Given two DTSs and some rules to match information items from one DTS to the other, the set of “technical differences” is unique, but the set of “semantic differences” is unlimited because they are just an interpretation of the “technical differences”. A “semantic difference” contains an aggregation of “technical differences” and human readable documentation that may be useful input to users migrating an application from using the previous taxonomy version to the next.
For the rest of this specification the phrase From DTS will be used to refer to the DTS that is being compared with the To DTS.
For the rest of this specification the phrase To DTS will be used to refer to the DTS being compared with the From DTS.
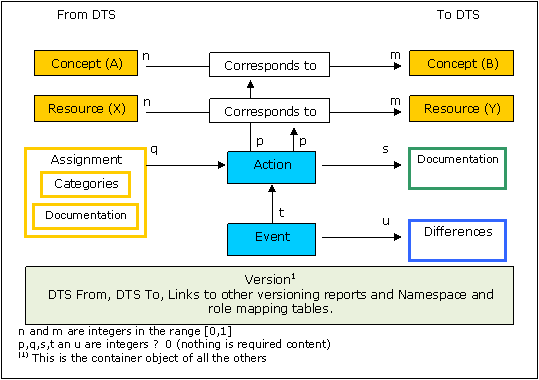
The following figure represents the different layers in which the information of a versioning report is structured.
Figure 1: source of information for a versioning report
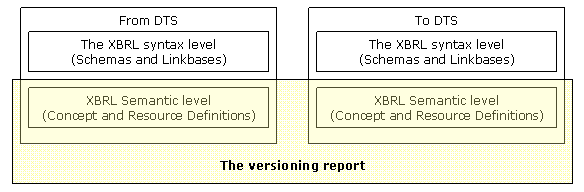
There are many examples that show how the information in a DTS can be written in one or many different files without any impact on applications using the DTS. A simple example:
o A taxonomy schema "A.XSD" for the namespace http://foo defining two concepts tx:One and tx:Two may reference one presentation linkbase with one parent-child arc in the http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role connecting the two concepts whereby tx:One is the parent of tx:Two.
o A different taxonomy schema "B.XSD" for the same namespace http://foo and defining the same concepts (tx:One and tx:Two), may have two embedded presentation linkbases in the same http://www.xbrl.org/2003/role role - one saying that tx:Two is the parent of tx:One and the other relationship prohibiting the previous relationship and creating another one saying that tx:One is the parent of tx:Two.
Both taxonomies are equivalent from the DTS consumer perspective because, even though taxonomy "A.XSD" and "B.XSD" are completely different in their syntaxes, both define the same concepts and the same resulting relationship between the concepts. Both DTSs define the same information set as it is used by applications consuming XBRL metadata other than, perhaps, XBRL Taxonomy editors that have more strict requirements about representing prohibited relationships to the user.
2.1 The XBRL versioning Infoset
The XBRL Infoset (Information Set) is an abstraction layer on top of the syntax layer. This abstraction layer expresses every information item in a DTS (concept definition, resource definition, relationship, etc) based on its property and not based on the syntax used to serialize it in XML Schemas or XBRL linkbases.
Versioning is built on top of the XBRL Infoset without making any reference to the actual underlying syntax. Of course, the relationship between the information item properties and the XBRL syntax exists and software tools can easily find and use it.
The XBRL versioning Infoset is a sub-set of the properties and objects defined in the XBRL Infoset. Not everything in the XBRL Infoset is related to concept definitions or resource definitions. The following table describes the set of items and properties in and out of the scope for a versioning report.
|
The DTS Information Item |
All properties are included. |
|
|
The XBRL Document Information Item |
[XIS 2.2.2] |
All properties are excluded[3]. |
|
The XBRL Taxonomy Information Item |
Namespace [XIS 2.2.3.2] is included. All other properties are excluded. |
|
|
The Imported Taxonomy Information Item |
[XIS 2.2.4] |
All excluded. |
|
The Role Type Information Item |
URI [XIS 2.2.5.4] is included. All other properties are excluded. |
|
|
The Arcrole Type Information Item |
URI [XIS 2.2.6.4] is included. All other properties are excluded. |
|
|
The Used On Information Item |
[XIS 2.2.7] |
All properties are excluded. |
|
The XBRL Concept Information Item |
All properties are included. |
|
|
The XBRL Item Information Item |
All properties are included. |
|
|
The XBRL Tuple Information Item |
All properties are included. |
|
|
The XBRL Linkbase Information Item |
[XIS 2.2.11] |
All properties are excluded. |
|
The Extended Link Information Item |
The role URI on extended links is used to define the relationship identifier. |
|
|
The Documentation Information Item |
[XIS 2.2.13] |
All properties are excluded. |
|
The Relationship Information Item |
Only relationships that exist after prohibition and overriding rules defined in the XBRL 2.1 specification are considered part of a concept definition. For those relationships, only the following properties are included: Type [XIS 2.2.14.2] From [XIS 2.2.14.3] To [XIS 2.2.14.4] Arcrole URI [XIS 2.2.6.4] Order [XIS 2.2.14.6] Priority [XIS 2.2.14.8] Attributes [XIS 2.2.14.9] |
|
|
The Resource Information item |
All resources in the DTS are considered. See section 2.4.3 below for more information. For resources, the following properties are included: Type [XIS 2.2.15.2] Role URI [XIS 2.2.5.4] Element [XIS 2.2.15.4] From [XIS 2.2.15.5] To [XIS 2.2.15.6] Attributes [XIS 2.2.15.7] Value [XIS 2.2.15.8] |
Changes to other properties that are not included in the list above can be documented in the versioning report despite the fact that they will not produce Diff Events [Def 1] according to this specification. The content model of the versioning report allows a report to contain specific documentation about a particular change and generic documentation not related to a particular change.
This specification defines the following additional properties that are derived from information that exists in the XBRL Information Set but not explicitly indicated as properties in the XIS documentation.
|
Preceding |
The Preceding property of an XBRL Relationship Information Item R is the set of XBRL Relationship Information Items RS that satisfies the following conditions: 1. R and RS belong to the same Extended Link role[4], and 2. R and RS have the same value in the type property [XIS 2.2.14.2], and 3. RS is positioned immediately before R in the set of relationships that satisfies conditions 1 and 2 ordered using the value of the order property [XIS 2.2.14.6]. |
|
|
Following |
The Following Relationship of an XBRL Relationship Information Item R is the set of XBRL Relationship Information Items RS that satisfies the following conditions: 1. R and RS belong to the same Extended Link role4, and 2. R and RS have the same value in the type property [XIS 2.2.14.2], and 3. RS is positioned immediately after R in the set of relationships that satisfies conditions 1 and 2 ordered using the value of the order property [XIS 2.2.14.6]. |
2.2 The differences between two DTSs
This specification defines the equivalency operation between two DTSs, the From DTS and the To DTS. The equivalency operation is independent of the syntax and modularization strategy used to serialize a DTS.
Two DTSs (From DTS and To DTS) are equivalent if there are no differences in the concept definitions and no differences in the resources defined in the DTSs.
Comparison of two DTSs that are not equivalent produces a set of technical differences that are identified in this specification. This specification does not pertain to define one specific algorithm to find the differences.
[Def 1] A Difference Event is the representation of something not equivalent found between properties of two corresponding XBRL Information Items being compared. This is equivalent to a “technical difference” as defined earlier in this document.
There are Difference Events defined for each type of “technical difference” that is possible between two XBRL Information Items covered by this specification.
The computation of the Difference Events requires two tables of paired properties that define the mapping rules between DTSs. See section 3.10 below and the definitions of namespace pair [Def 5] and role URI pair [Def 6]. Some properties must be compared after applying the appropriate mapping. This specification explicitly defines in which situation the mapping rules must be applied.
Some of the “technical differences” between two concept definitions or resource definitions can only be represented using a set of correlated difference events. This is for example the case of changes in attributes of a relationship that requires the following set of events:
[EvConceptRelationshipFrom] event with two parameters Error! Reference source not found. pointing to the From and To concepts. This event will be the starting event and the parent of,
[EvRelationshipAttribute] event with parameters Error! Reference source not found. pointing to the From and To relationships where an attribute has been changed. This event will be the parent of,
[EvAttributesInequality] event with parameters Error! Reference source not found. pointing to the From and To attribute whose values are not equal. This one will be the Ending event in the path.
[Def 2] A Difference Path is a set of Difference Events. Some of the events contain parameters to identify the concepts, relationships, resources, attributes or XML fragments.
[Def 3] The Starting Event of a path is always the first event in the path.
[Def 4] The Ending Event of a path is always the last event in the path.
A Difference Path contains just one starting event and one ending event. It is possible that the path contains just one event that plays the role of starting and ending event simultaneously. A Difference Path is not a tree with one starting event and multiple ending events.
The set of possible ending events is enumerated in section 2.5 below.
The set of possible starting events are those defined in sections 2.2.1, 2.2.2, 2.2.3 or 2.2.5 below.
2.2.1 Comparing two DTS Information Items:
Two DTS Information Items [XIS 2.2.1] D1 (the From DTS) and D2 (the To DTS) are equivalent if both the following conditions are satisfied and none of the “NOT equivalent” conditions below exist:
1. For each XBRL Concept Information Item [XIS 2.2.8] defined in the Concepts
property [XIS
2.2.1.2] of D1 there
exists a corresponding XBRL Concept Information
item [XIS 2.2.8] in D2;
both items are equivalent if they satisfy all conditions in section 2.2.2 or 2.2.3
below.
2. For each XBRL Resource Information Item [XIS 2.2.15] defined in the Resources property [XIS 2.2.1.3] of D1 where a corresponding XBRL Resource Information Item [XIS 2.2.15] is found in D2; both items are equivalent if they satisfy all conditions in section 2.2.5 below.
Two DTS Information Items [XIS 2.2.1] D1 (the From DTS) and D2 (the To DTS) are NOT equivalent if any of the following conditions exist:
1. For any XBRL Concept Information Item [XIS 2.2.8] defined in the Concepts property [XIS 2.2.1.2] of D1 there does not exist any corresponding XBRL Concept Information item [XIS 2.2.8] in D2,. Processors MUST document all such differences by generating a Concept deleted event [EvConceptDelete] with the concept identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [from DTS] parameter.
2. For any XBRL Concept Information Item [XIS 2.2.8] defined in the Concepts property [XIS 2.2.1.2] of D2 a corresponding XBRL Concept Information item [XIS 2.2.8] cannot be found in D1. Processors MUST document all such differences by generating a Concept added event [EvConceptNew] with the concept identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [to DTS] parameter.
3. For any XBRL Resource Information Item [XIS 2.2.15] defined in the Resources property [XIS 2.2.1.3] of D1 a corresponding XBRL Resource Information Item [XIS 2.2.15] cannot be found in D2. Processors MUST document all such differences generating a Resource deleted event [EvResourceDelete] with the resource identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [from DTS] parameter.
4. For any XBRL Resource Information Item [XIS 2.2.15] defined in the Resources property [XIS 2.2.1.3] of D2 a corresponding XBRL Resource Information Item [XIS 2.2.15] cannot be found in D1. Processors MUST document any such differences generating a Resource added event [EvResourceNew] with the resource identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [to DTS] parameter.
2.2.2 Comparing two XBRL Item Information Items:
Two XBRL Item Information Items [XIS 2.2.9] I1, which belongs to the From DTS, and I2, which belongs to the To DTS, are equivalent if all the following conditions are satisfied and none of the “NOT equivalent” conditions below exist:
1. If the value of the Namespace property [XIS 2.2.3.2] of the XBRL Taxonomy Information Item [XIS 2.2.3] referenced in the Parent property [XIS 2.2.8.1] of I1 is equal to the value of the namespace pair [Def 5] of the Namespace property [XIS 2.2.3.2] of the XBRL Taxonomy Information Item [XIS 2.2.3] referenced in the Parent property [XIS 2.2.8.1] of I2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept namespace event [EvConceptNamespace] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
2. If the value of the Name property [XIS 2.2.8.2] of I1 is equal to the value of the Name property [XIS 2.2.8.2] of I2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept name event [EvConceptName] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
3. If the content of the Type property [XIS 2.2.8.3] of I1 is equivalent to the content of the Type property [XIS 2.2.8.3] of I2 according to section 2.2.8 below this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept Type event [EvConceptType] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
4. If the value of the Substitution Group property [XIS 2.2.8.4] of I1 is equal to the value of the Substitution Group property [XIS 2.2.8.4] of I2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept Substitution Group event [EvSubstitutionGroup] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
5. If the value of the Period Type property [XIS 2.2.9.2] of I1 is equal to the value of the Period Type property [XIS 2.2.9.2] of I2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept Period Type event [EvPeriodType] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
6. If the value of the Balance property [XIS 2.2.9.3] of I1 is equal to the value of the Balance property [XIS 2.2.9.3] of I2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept Balance event [EvBalance] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
7. If the value of the Default property [XIS 2.2.9.4] of I1 is equal to the value of the Default property [XIS 2.2.9.4] of I2. If this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept Default event [EvDefault] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
8. If the value of the Nillable property [XIS 2.2.8.5] of I1 is equal to the value of the Nillable property [XIS 2.2.8.5] of I2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept Nillable event [EvNillable] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
9. If the value of the Abstract property [XIS 2.2.8.6] of I1 is equal to the value of the Abstract property [XIS 2.2.8.6] of I2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept Abstract event [EvAbstract] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
10. If the value of the Block property [XIS 2.2.8.7] of I1 is equal to the value of the Block property [XIS 2.2.8.7] of I2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept Block event [EvBlock] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
11. If the value of the Fixed property [XIS 2.2.8.8] of I1 is equal to the value of the Fixed property [XIS 2.2.8.8] of I2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept Fixed event [EvFixed] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
12. If the value of the Final property [XIS 2.2.8.9] of I1 is equal to the value of the Final property [XIS 2.2.8.9] of I2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept Final event [EvFinal] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
13. For each XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the From property [XIS 2.2.8.10] of I1 where a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the From property [XIS 2.2.8.10] of I2 exist; both relationships are equivalent if they satisfy all conditions in section 2.2.4 below. Processors MUST raise a Concept From event [EvConceptRelationshipFrom] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied. This event will be the parent of additional events according to section 2.2.4 below.
14. For each XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the To property [XIS 2.2.8.11] of I1 where a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the To property [XIS 2.2.8.11] of I2 exists; both relationships are equivalent if they satisfy all conditions in section 2.2.4 below. Processors MUST raise a Concept To event [EvConceptRelationshipTo] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied. This event will be the parent of additional events according to section 2.2.4 below.
15. For each XML Attribute Information Item in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.8.12] of I1 where a corresponding XML Attribute Information Item in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.8.12] of I2 exists; both attributes are equivalent if they satisfy all conditions in section 2.2.7 below. Processors MUST raise a Concept Attribute event [EvConceptAttribute] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied. This event will be the parent of additional events according to section 2.2.7 below.
16. For each XML Element Information Item in the Children property [XIS 2.2.8.13] of I1 where a corresponding XML Element Information Item in the Children property [XIS 2.2.8.13] of I2 exists; both XML Elements are equivalent if they satisfy all conditions in section 2.2.6 below. Processors MUST raise a Concept Child event [EvChild] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied. This event will be the parent of additional events according to section 2.2.6 below.
Two XBRL Item Information Items [XIS 2.2.9] I1, which belongs to the From DTS, and I2, which belongs to the To DTS, are NOT equivalent if any of the following conditions exist:
1. For any XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the From property [XIS 2.2.8.10] of I1 a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] cannot be found in the From property [XIS 2.2.8.10] of I2. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Concept From event [EvConceptRelationshipFrom] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Relationship deleted event [EvRelationshipDelete] with the relationship identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [From DTS] parameter.
2. For any XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the From property [XIS 2.2.8.10] of I2 a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] cannot be found in the From property [XIS 2.2.8.10] of I1. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Concept From event [EvConceptRelationshipFrom] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Relationship added event [EvRelationshipNew] with the relationship identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [To DTS] parameter.
3. For any XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the To property [XIS 2.2.8.11] of I1 a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] cannot be found in the To property [XIS 2.2.8.11] of I2. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Concept To event [EvConceptRelationshipTo] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Relationship deleted event [EvRelationshipDelete] with the relationship identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [From DTS] parameter.
4. For any XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the To property [XIS 2.2.8.11] of I2 a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] cannot be found in the To property [XIS 2.2.8.11] of I1. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Concept To event [EvConceptRelationshipTo] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Relationship added event [EvRelationshipNew] with the relationship identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [To DTS] parameter.
5. For any XML Attribute Information Item in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.8.12] of I1 a corresponding XML Attribute Information Item cannot be found in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.8.12] of I2. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Concept Attribute event [EvConceptAttribute] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by an Attribute deleted event [EvAttributeDelete] with the attribute identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [From DTS] parameter.
6. For any XML Attribute Information Item in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.8.12] of I2 a corresponding XML Attribute Information Item cannot be found in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.8.14] of I1. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Concept Attribute event [EvConceptAttribute] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by an Attribute added event [EvAttributeNew] with the attribute identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [To DTS] parameter.
7. For any XML Element Information Item in the Children property [XIS 2.2.8.13] of I1 a corresponding XML Element Information Item cannot be found in the Children property [XIS 2.2.8.13] of I2. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Concept Child event [EvChild] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Element node deleted event [EvNodeDeleted] with the XML element identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [From DTS] parameter.
8. For any XML Element Information Item in the Children property [XIS 2.2.8.13] of I2 a corresponding XML Element Information Item cannot be found in the Children property [XIS 2.2.8.13] of I1. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Concept Child event [EvChild] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Element node added event [EvNodeNew] with the XML element identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [To DTS] parameter.
2.2.3 Comparing two XBRL Tuple Information Items:
Two XBRL Tuple Information Items [XIS 2.2.10] T1, which belongs to the From DTS, and T2, which belongs to the To DTS, are equivalent if all the following conditions are satisfied and none of the “NOT equivalent” conditions below exist.
1. If the value of the Namespace property [XIS 2.2.3.2] of the XBRL Taxonomy Information Item [XIS 2.2.3] referenced in the Parent property [XIS 2.2.8.1] of T1 is equal to the value of the namespace pair [Def 5] of the Namespace property [XIS 2.2.3.2] of the XBRL Taxonomy Information Item [XIS 2.2.3] referenced in the Parent property [XIS 2.2.8.1] of T2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept namespace event [EvConceptNamespace] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
2. If the value of the Name property [XIS 2.2.8.2] of T1 is equal to the value of the Name property [XIS 2.2.8.2] of T2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept name event [EvConceptName] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
3. If the content of the Type property [XIS 2.2.8.3] of T1 is equivalent to the content of the Type property [XIS 2.2.8.3] of T2 according to section 2.2.8 below this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept Type event [EvConceptType] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
4. If the value of the Substitution Group property [XIS 2.2.8.4] of T1 is equal to the value of the Substitution Group property [XIS 2.2.8.4] of T2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept Substitution Group event [EvSubstitutionGroup] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
5. If the value of the Nillable property [XIS 2.2.8.5] of T1 is equal to the value of the Nillable property [XIS 2.2.8.5] of T2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept Nillable event [EvNillable] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
6. If the value of the Abstract property [XIS 2.2.8.6] of T1 is equal to the value of the Abstract property [XIS 2.2.8.6] of T2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept Abstract event [EvAbstract] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
7. If the value of the Block property [XIS 2.2.8.7] of T1 is equal to the value of the Block property [XIS 2.2.8.7] of T2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept Block event [EvBlock] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
8. If the value of the Final property [XIS 2.2.8.9] of T1 is equal to the value of the Final property [XIS 2.2.8.9] of T2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Concept Final event [EvFinal] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
9. For each XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the From property [XIS 2.2.8.10] of T1 where a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the From property [XIS 2.2.8.10] of T2 exist; both relationships are equivalent if they satisfy all conditions in section 2.2.4 below. Processors MUST raise a Concept From event [EvConceptRelationshipFrom] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied. This event will be the parent of additional events according to section 2.2.4 below.
10. For each XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the To property [XIS 2.2.8.11] of T1 where a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the To property [XIS 2.2.8.11] of T2 exists; both relationships are equivalent if they satisfy all conditions in section 2.2.4 below. Processors MUST raise a Concept To event [EvConceptRelationshipTo] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied. This event will be the parent of additional events according to section 2.2.4 below.
11. For each XML Attribute Information Item in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.8.12] of T1 where a corresponding XML Attribute Information Item in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.8.12] of T2 exists; both attributes are equivalent if they satisfy all conditions in section 2.2.7 below. Processors MUST raise a Concept Attribute event [EvConceptAttribute] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied. This event will be the parent of additional events according to section 2.2.7 below.
12. For each XML Element Information Item in the Children property [XIS 2.2.8.13] of T1 where a corresponding XML Element Information Item in the Children property [XIS 2.2.8.13] of T2 exists; both XML Elements are equivalent if they satisfy all conditions in section 2.2.6 below. Processors MUST raise a Concept Child event [EvChild] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied. This event will be the parent of additional events according to section 2.2.6 below.
Two XBRL Tuple Information Items [XIS 2.2.10] T1, which belongs to the From DTS, and T2, which belongs to the To DTS, are NOT equivalent if any of the following conditions exist.
1. For any XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the From property [XIS 2.2.8.10] of T1 a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] cannot be found in the From property [XIS 2.2.8.10] of T2. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Concept From event [EvConceptRelationshipFrom] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Relationship deleted event [EvRelationshipDelete] with the relationship identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [From DTS] parameter.
2. For any XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the From property [XIS 2.2.8.10] of T2 a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] cannot be found in the From property [XIS 2.2.8.10] of T1. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Concept From event [EvConceptRelationshipFrom] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Relationship added event [EvRelationshipNew] with the relationship identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [To DTS] parameter.
3. For any XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the To property [XIS 2.2.8.11] of T1 a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] cannot be found in the To property [XIS 2.2.8.11] of T2. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Concept To event [EvConceptRelationshipTo] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Relationship deleted event [EvRelationshipDelete] with the relationship identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [From DTS] parameter.
4. For any XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the To property [XIS 2.2.8.11] of T2 a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] cannot be found in the To property [XIS 2.2.8.11] of T1. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Concept To event [EvConceptRelationshipTo] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Relationship added event [EvRelationshipNew] with the relationship identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [To DTS] parameter.
5. For any XML Attribute Information Item in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.8.12] of T1 a corresponding XML Attribute Information Item cannot be found in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.8.12] of T2. In this case, Processors MUST raise an Concept Attribute event [EvConceptAttribute] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by an Attribute deleted event [EvAttributeDelete] with the attribute identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [From DTS] parameter.
6. For any XML Attribute Information Item in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.8.12] of T2 a corresponding XML Attribute Information Item cannot be found in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.8.12] of T1. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Concept Attribute event [EvConceptAttribute] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by an Attribute added event [EvAttributeNew] with the attribute identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [To DTS] parameter.
7. For any XML Element Information Item in the Children property [XIS 2.2.8.13] of T1 where a corresponding XML Element Information Item cannot be found in the Children property [XIS 2.2.8.13] of T2. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Concept Child event [EvChild] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Element node deleted event [EvNodeDeleted] with the XML element identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [From DTS] parameter.
8. For any XML Element Information Item in the Children property [XIS 2.2.8.13] of T2 where a corresponding XML Element Information Item cannot be found in the Children property [XIS 2.2.8.13] of T1. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Concept Child event [EvChild] with the two concept identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Element node added event [EvNodeNew] with the XML element identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [To DTS] parameter.
2.2.4 Comparing two XBRL Relationship Information Items:
Two XBRL Relationship Information Items [XIS 2.2.14] R1, which belongs to the From DTS, and R2, which belongs to the To DTS, are equivalent if all the following conditions are satisfied and none of the “NOT equivalent” conditions below exist.
1. If the object in the From DTS pointed to by the From property [XIS 2.2.14.3] of R1 corresponds to the object in the To DTS pointed to by the From property [XIS 2.2.14.2] of R2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST add a Relationship Source event [EvSource] to the parent event with the two relationship identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
2. If the object in the From DTS pointed to by the To property [XIS 2.2.14.4] of R1 corresponds to the object in the To DTS pointed to by the To property [XIS 2.2.14.4] of R2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST add a Relationship Target event [EvTarget] to the parent event with the two relationship identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
3. If each relationship in the relationship set that precedes R1 [XVS 2.1.1] in the From DTS corresponds to another relationship in the relationship set that precedes R2 [XVS 2.1.1] in the To DTS, or both relationships have no preceding relationship set this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST add a Relationship Previous event [EvPrevious] to the parent event with the two relationship identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
4. If each relationship in the relationship set that follows R1 [XVS 2.1.2] in the From DTS corresponds to another relationship in the relationship set that follows R2 [XVS 2.1.2] in the To DTS, or both relationships have no a following relationship set this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST add a Relationship Next event [EvNext] to the parent event with the two relationship identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
5. If the value of the Priority property [XIS 2.2.14.8] of R1 is equal to the value of the Priority property [XIS 2.2.14.8] of R2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST add a Relationship Priority event [EvPriority] to the parent event with the two relationship identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
6. For each XML Attribute Information Item in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.14.9] of R1 where a corresponding XML Attribute Information Item in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.14.9] of R2 exists; both attributes are equivalent if they satisfy all conditions in section 2.2.7 below. Processors MUST add a Relationship Attribute event [EvRelationshipAttribute] with the two relationship identifiers Error! Reference source not found. to the parent event if this condition is not satisfied. This event will be the parent of additional events according to section 2.2.7 below.
Two XBRL Relationship Information Items [XIS 2.2.14] R1, which belongs to the From DTS, and R2, which belongs to the To DTS, are NOT equivalent if any of the following conditions exist.
1. For any XML Attribute Information Item in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.14.9] of R1 a corresponding XML Attribute Information Item cannot be found in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.14.9] of R2. In this case, Processors MUST add a Relationship Attribute event [EvRelationshipAttribute] with the two relationship identifiers Error! Reference source not found. to the parent event followed by a Attribute deleted event [EvAttributeDelete] with the attribute identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [From DTS] parameter.
2. For any XML Attribute Information Item in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.14.9] of R2 a corresponding XML Attribute Information Item cannot be found in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.14.9] of R1. In this case, Processors MUST add a Relationship Attribute event [EvRelationshipAttribute] with the two relationship identifiers Error! Reference source not found. to the parent event followed by a Attribute added event [EvAttributeNew] with the attribute identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [To DTS] parameter.
2.2.5 Comparing two XBRL Resource Information Items:
Two XBRL Resource Information Items [XIS 2.2.15] X1, which belongs to the From DTS, and X2, which belongs to the To DTS, are equivalent if all the following conditions are satisfied and none of the “NOT equivalent” conditions below exist:
1. If the value of the Type property [XIS 2.2.15.2] of X1 is equal to the value of the Type property [XIS 2.2.15.2] of X2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Resource Type event [EvResourceType] with the two resource identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
2. If the value of the URI property [XIS 2.2.5.4] of the XBRL Role Type Information Item [XIS 2.2.5] referenced in the Role property [XIS 2.2.15.3] of X1 is equal to the value of the value of the URI property [XIS 2.2.5.4] of the XBRL Role Type Information Item [XIS 2.2.5] referenced in the Role property [XIS 2.2.15.3] of X2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Resource Role event [EvRole] with the two resource identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
3. For each XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the From property [XIS 2.2.15.5] of X1 where a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the From property [XIS 2.2.15.5] of X2 exist; both relationships are equivalent if they satisfy all conditions in section 2.2.4 above. Processors MUST raise a Resource From event [EvResourceFrom] with the two resource identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied. This event will be the parent of additional events according to section 2.2.4 above.
4. For each XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the To property [XIS 2.2.15.6] of X1 where a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the To property [XIS 2.2.15.6] of X2 exists; both relationships are equivalent if they satisfy all conditions in section 2.2.4 above. Processors MUST raise a Resource To event [EvResourceTo] with the two resource identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied. This event will be the parent of additional events according to section 2.2.4 above.
5. For each XML Attribute Information Item in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.15.7] of X1 where a corresponding XML Attribute Information Item in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.15.7] of X2 exists; both attributes are equivalent if they satisfy all conditions in section 2.2.7 below. Processors MUST raise a Resource Attribute event [EvResourceAttribute] with the two resource identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied. This event will be the parent of additional events according to section 2.2.7 below.
6. If the resource has complex content and for each node N1 in the sequence of nodes of the Element property [XIS 2.2.15.4] of X1; a node N2 exist that is the node in the same position in the sequence of nodes in the Element property [XIS 2.2.15.4] of X2 and N1 is s-equal2 to the node N2 (except for the attributes in the XLINK namespace and the id attributes that must be skipped) this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Resource Content event [EvContent] with the two resource identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied. This event will be the parent of additional events according to section 2.2.6 below.
7. If the resource has simple content and the value of the Value property [XIS 2.2.15.8] of X1 is s-equal2 to the value of the Value property [XIS 2.2.15.8] of X2 this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST raise a Resource Value event [EvValue] with the two resource identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
Two XBRL Resource Information Items [XIS 2.2.15] X1, which belongs to the From DTS, and X2, which belongs to the To DTS, are NOT equivalent if any of the following conditions exist:
8. For any XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the From property [XIS 2.2.15.5] of X1 a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] cannot be found in the From property [XIS 2.2.15.5] of X2. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Resource From event [EvResourceFrom] with the two resource identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Relationship deleted event [EvRelationshipDelete] with the relationship identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [From DTS] parameter.
9. For any XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the From property [XIS 2.2.15.5] of X2 a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] cannot be found in the From property [XIS 2.2.15.5] of X1. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Resource From event [EvResourceFrom] with the two resource identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Relationship added event [EvRelationshipNew] event with the relationship identifier Error! Reference source not found. as a parameter.
10. For any XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the To property [XIS 2.2.15.6] of X1 a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] cannot be found in the To property [XIS 2.2.15.6] of X2. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Resource To event [EvResourceTo] with the two resource identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Relationship deleted event [EvRelationshipDelete] with the relationship identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [From DTS] parameter.
11. For any XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] in the To property [XIS 2.2.15.6] of X2 a corresponding XBRL Relationship Information Item [XIS 2.2.14] cannot be found in the To property [XIS 2.2.15.6] of X1. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Resource To event [EvResourceTo] with the two resource identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Relationship added event [EvRelationshipNew] with the relationship identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [To DTS] parameter.
12. For any XML Attribute Information Item in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.15.7] of X1 a corresponding XML Attribute Information Item cannot be found in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.15.7] of X2. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Resource Attribute event [EvResourceAttribute] with the two resource identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by an Attribute deleted event [EvAttributeDelete] with the attribute identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [From DTS] parameter.
13. For any XML Attribute Information Item in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.15.7] of X2 a corresponding XML Attribute Information Item cannot be found in the Attributes property [XIS 2.2.15.7] of X1. In this case, Processors MUST raise a Resource Attribute event [EvResourceAttribute] with the two resource identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by a Attribute added event [EvAttributeNew] with the attribute identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [To DTS] parameter.
14. For any resource that has complex content and for each node N1 in the sequence of nodes of the Element property [XIS 2.2.15.4] of X1 a node N2 that is the node in the same position in the sequence of nodes in the Element property [XIS 2.2.15.4] of X2 does not exist. In this case, a Processor MUST raise a Resource Content event [EvContent] with the two resource identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by an Element node deleted event [EvNodeDeleted] with the XML Element Identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [From DTS] parameter.
15. For any resource that has complex content and for each node N2 in the sequence of nodes of the Element property [XIS 2.2.15.4] of X2 a node N1 that is the node in the same position in the sequence of nodes in the Element property [XIS 2.2.15.4] of X1 does not exist. In this case, a Processor MUST raise a Resource Content event [EvContent] with the two resource identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters followed by an Element node added event [EvNodeNew] with the XML Element Identifier Error! Reference source not found. in the [To DTS] parameter.
2.2.6 Comparing two XML Element Information Items:
Two XML Element Information Items E1, which belongs to the From DTS and E2, which belongs to the To DTS, are equivalent if the following condition is satisfied:
1. If E1 and E2 are s-equal2 nodes except for the attributes in the XLINK namespace and the id attribute this condition is satisfied. Processors MUST add a Not s-equal2 nodes event [EvNodesInequality] to the parent event with the two element identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
2.2.7 Comparing two XML Attribute Information Items:
Two XML Attribute Information items A1,which belongs to the From DTS and A2, which belongs to the To DTS are equivalent if the following condition is satisfied:
2. If A1 and A2 are s-equal2 nodes this condition is satisfied. The s-equal2 predicate is defined in section 2.3 below. Processors MUST raise a Not s-equal2 attributes event [EvAttributesInequality] to the parent event with the two attribute identifiers Error! Reference source not found. as parameters if this condition is not satisfied.
2.2.8 Comparing two Schema Type Definitions:
This document does not impose any specific XSD object model, but the definition of equality of two XML types is necessary in order to properly implement a mechanism that identifies if an item, tuple or resource definition has changed from one taxonomy version to another.
Therefore, it is the responsibility of the vendor specific object model to provide information about the equality of item, tuple and resource data types.
As long as two different XSD data types are recognized as not equal, the amount of information provided about the differences is vendor dependant.
The XVS conformance suite provides a minimum set of test cases about differences in data type definitions. Processors MUST recognize changes in XSD data types at least for the use cases defined in the XVS conformance suite.[HW1] [ihr2]
2.3 Definition of the s-equal2 predicate between two sequences of XML nodes:
The s-equal2 predicate is identical
to the s-equal predicate defined in section 4.10 of the [XBRL] specification replacing XPath 1.0 with XPath
IMPLEMENTATION NOTE (non-normative): The [XBRL] 2.1 specification is based on XPath 1.0. According to
section 5.3 of the XPath 1.0 specification, the content of attributes is always
a string-value rather than a QName. XBRL APIs implementing the
equivalence operation between XML Information Items should take care of this
and normalize the prefixes of QNames in order to effectively compare QNames and not their lexical representation.
2.4 Rules of correspondence between Information Items
Section 2.2 of this specification compares two information items that correspond one (in the From DTS) to the other (in the To DTS). Only two information items that correspond are subject to be compared to detect “technical differences”. The rules of correspondence of two information items are described in this section.
Two information items A and B correspond if they are of the same type and satisfy all conditions in the.appropriate section according to the information item type.
2.4.1 Correspondence of Concept Definitions
Two concept definitions A and B are in correspondence if there is at least one Diff Event [Def 1] in the versioning report that contains the concept identifier Error! Reference source not found. of concept A in the [From DTS] parameter and the concept identifier Error! Reference source not found. of concept B in the [To DTS] parameter.
2.4.2 Correspondence of Relationships
Two relationships A and B are in correspondence if all the following conditions are satisfied:
· The correspondent Information Item of the content of the From property [XIS 2.2.14.3] of relationship A is the Information Item in the content of the From property [XIS 2.2.14.3] of relationship B. For the identification of the correspondent content in the From property [XIS 2.2.14.3] of the relationship A the appropriate section 2.4.1, 2.4.3 or 2.4.5 must be used according to the content type, and
· The URI pair [Def 6] of the URI property [XIS 2.2.5.4] of the role property [XIS 2.2.12.3] of the Extended Link [XIS 2.2.12] that is the Parent property [XIS 2.2.14.1] of the relationship A is equal to the value of the URI property [XIS 2.2.5.4] of the role property [XIS 2.2.12.3] of the Extended Link [XIS 2.2.12] that is the Parent property [XIS 2.2.14.1] of the relationship B, and
· The Type property [XIS 2.2.14.2] of relationship A is equal to the Type property [XIS 2.2.14.2] of relationship B, and
· The URI property [XIS 2.2.6.4] of the Arcrole property [XIS 2.2.14.5] of relationship A is equal to the URI property [XIS 2.2.6.4] of the Arcrole property [XIS 2.2.14.5] of relationship B, and
· The correspondent Information Item of the content of the To property [XIS 2.2.14.4] of relationship A is the Information Item in the content of the To property [XIS 2.2.14.4] of relationship B. For the identification of the correspondent content in the To property [XIS 2.2.14.4] of the relationship A the appropriate section 2.4.1, 2.4.3 or 2.4.5 must be used according to the content type.
2.4.3 Correspondence of Resources
Two resources A and B are in correspondence if there is at least one Diff Event [Def 1] in the versioning report that contains the resource identifier Error! Reference source not found. of resource A in the [From DTS] parameter and the resource identifier Error! Reference source not found. of resource B in the [To DTS] parameter.
2.4.4 Correspondence of XML Attributes
Two Attribute Information Items A1 and A2 are in correspondence if their node names are equal. The attribute value is not used to find the correspondent attribute of another attribute.
2.4.5 Correspondence of XML Element Nodes
Two XML Element nodes N1 and N2 are in correspondence if they are s-equal2 nodes.