1 Goals
XBRL provides a set of standard data types that may appear in XBRL schemas. These include those specified in [XBRL 2.1], [DIMENSIONS] and any additional modules that are XBRL RECOMMENDATIONs. As XBRL applications emerge, new, non-standard data types having common and useful semantics are being proposed. The goal of the XBRL Data Type Registry DTR is to be a public, online data set that documents these non-standard data types and their usage. Additions and other changes to the DTR, like other XBRL International work products, are processed through a series of steps detailed in this document. The goal is to maximise the utility and longevity of the new data types and the taxonomies that use them.
1.1 Relationship to other work
This document pertains to XBRL as defined in the XBRL Specification [XBRL 2.1] and additional modules such as [DIMENSIONS].
1.2 Terminology
The key words MUST, MUST NOT, REQUIRED, SHALL, SHALL NOT, SHOULD, SHOULD NOT, RECOMMENDED, MAY, and OPTIONAL, in this specification, are to be interpreted as described in [IETF RFC 2119].
abstract element, bind, concept, concrete element, context, Discoverable Taxonomy Set (DTS), duplicate items, duplicate tuples, element, entity, equal, essence concept, fact, instance, item, least common ancestor, linkbase, period, taxonomy, tuple, unit, taxonomy schema, child, parent, sibling, grandparent, uncle, ancestor, XBRL instance, c-equal, p-equal, s-equal, u-equal, v-equal, x-equal, minimally conforming XBRL processor, fully conforming XBRL processor and any other terms not specifically defined elsewhere in this document but which are used and defined in the XBRL 2.1 specification. are as defined by [XBRL 2.1] .
BPB refers to the XBRL International Best Practices Board .
CR refers to a Candidate Recommendation of XBRL International.
ISC refers to the XBRL International Steering Committee .
IWD refers to an Internal Working Draft of XBRL International.
DTR refers to the Data Types Registry that is the subject of this specification.
DTRAM refers to the Data Types Registry Approval Manager.
PWD refers to a Public Working Draft of XBRL International.
Referee is either the SWG, TRTF or TAPWG when performing an evaluation requested by the DTRAM.
SWG refers to the XBRL International Base Specification and Maintenance Working Group.
TAPWG refers to the Taxonomy Architecture Practice Working Group set up by the BPB.
TRTF refers to the Taxonomy Review Task Force set up by the BPB.
XSB refers to the XBRL International Standards Board .
1.3 Language
The official language of XBRL International's own work products is English and the preferred spelling convention is UK English.
All documentation supporting a registry entry MUST be provided in English, and MAY be provided in additional languages.
1.4 Document conventions
1.4.1 Typographic conventions
1.4.1.2 Footnote notation
Comments which are informative, but not essential to the understanding of the point at hand, are provided in footnotes. All footnotes are non-normative.
1.4.1.3 Element and attribute notation
When referring to a specific element, it will be identified by
its namespace prefix and local name. For example, the root element
of a versioning report would be referred to as <ver:report> .
Attributes are also identified by their local name and, where
appropriate, their namespace prefix. Attributes are
distinguished from elements by prefixing them by an
@
symbol. Thus,
@id
refers to the attribute with the name id.
When referring to any attribute, so long as it has a specific
namespace, the local name is replaced by an asterisk (
*).
Thus, the notation @xml:* specifies any attribute
in the namespace
http://www.w3.org/XML/1998/namespace.
1.4.2 Formatting conventions
The following highlighting is used for normative technical material in this document:
Text of the normative example.
The following highlighting is used for non-normative examples in this document:
Text of the non-normative example.
The following highlighting is used for non-normative examples of poor, discouraged or disallowed usage.
Text of the discouraged example.
2 Update Process
The process by which an entry is added to the DTR is described below. This is modelled on [TECH-WG-PROCESSES] but is shortened to reflect the fact that the nature of an DTR entry is significantly less pervasive than that of a specification or other work product that is the usual output of a Working Group.
In addition a "fast track" process is provided whereby data types that do not necessarily have general applicability (and so are unlikely to qualify for RECOMMENDED status) can nevertheless be included in the DTR as "Acknowledged".
The process starts when the submitter creates a submission containing all of the information needed (as specified in [DTR STRUCTURE]) and requests the DTRAM to enter it into the DTR. The submitter MUST indicate whether they are seeking Acknowledged or RECOMMENDATION status. If they are seeking Acknowledged status then the subsequent steps are as detailed in Section 2.1, if they are seeking RECOMMENDATION status then the subsequent steps are as detailed in Section 2.2.
Submitters should note that the initial status of their submission MUST be "PROPOSED" (see [DTR STRUCTURE]).
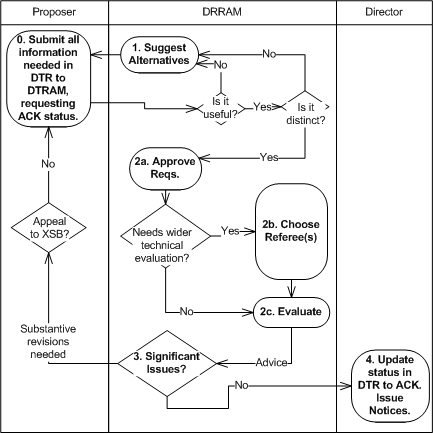
2.1 Steps to achieve Acknowledged status
A "fast track" process is provided to facilitate the inclusion of a data type in the DTR which may not have general applicability but which the submitter would, nevertheless, like to have documented in a publicly accessible fashion. A data type that successfully follows this "fast track" process will have an ending status of "ACK". As such it does not carry the same normative weight as a data type with "REC" status.
- The DTRAM MAY suggest alternatives to the proposal and request to its editors that it be resubmitted as they see fit. In the event that there is more than one submission made for similar requirements, or if the submission is substantially similar to an entry that is already present in the DTR the DTRAM may request the submitters to agree a common solution between themselves and resubmit a single joint submission. If this is not acceptable to the submitters the XSB will be requested to arbitrate. In any event a submitted type MUST NOT have the same local name as any other type already in the registry, regardless of namespace.
- The DTRAM approves the requirements and conducts a technical evaluation. If the DTRAM determines that wider technical evaluation is necessary they MAY then refer the submission to any or all (at their discretion) of the SWG, the TRTF or the TAPWG (hereinafter the referee) for such technical evaluation.
- If there are significant objections or problems arising as a result of this evaluation the DTRAM MAY request the submitter to address such issues. The submitter may then either modify the submission and resubmit, withdraw the submission, or appeal to the XSB.
- If there are no significant objections or problems arising as a result of this evaluation the data type is entered into the DTR with a status of "ACK" and the process is complete.
 |
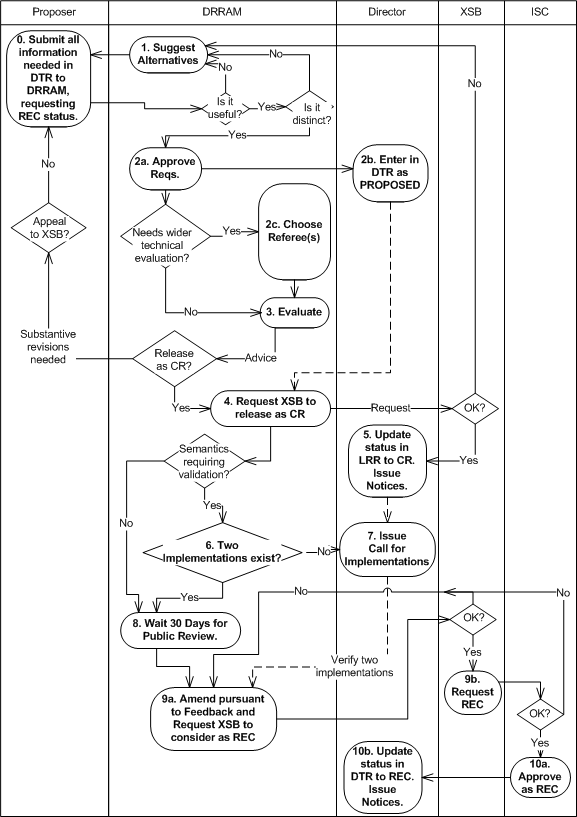
2.2 Steps to achieve RECOMMENDATION status
A data type that follows this track will have a status that is normative to the extent documented in Section 4 ("Normative Status of Data Types in the DTR and Software") of [DTR STRUCTURE]. Thus the process is, necessarily, considerably more rigorous than for a data type that follows the "fast track" process leading to "Acknowledged status".
- The DTRAM MAY suggest alternatives to the proposal and request to its editors that it be resubmitted as they see fit. In the event that there is more than one submission made for similar requirements, or if the submission is substantially similar to an entry that is already present in the DTR the DTRAM MAY request the submitters to agree a common solution between themselves and resubmit a single joint submission. If this is not acceptable to the submitters the XSB will be requested to arbitrate.
- The DTRAM approves the requirements and conducts a technical evaluation. This shall include an initial check that no submitted type has the same local name as any other type already in the registry, regardless of namespace. Provided this initial check is passed the entry is added to the DTR with a status of "PROPOSED". If the DTRAM determines that wider technical evaluation is necessary they MAY then refer the submission to any or all (at their discretion) of the SWG, the TRTF or the TAPWG (hereinafter the referee) for such technical evaluation.
- If requested in the previous step the referee deliberates the submission. If they are satisified then they recommend to the DTRAM that they approve release of the submission as a CR. If they are not satisfied they advise the DTRAM giving their reasons. The DTRAM in turn notifies the submitter who MAY then either modify the submission and resubmit, withdraw the submission, or appeal to the XSB.
- The DTRAM approves the submission and recommends to the XSB that it be released as a CR. (Note that, in the interests of a speedy process, this bypasses the PWD step of [TECH-WG-PROCESSES]).
- Upon approval of such publication by the XSB, the DTRAM updates its status in the DTR to CR. A notice of this change is made in the same way as such notices are published according to [TECH-WG-PROCESSES] and feedback requested.
- The DTRAM or, if they decide to delegate this step, the referee verifies that the conformance suite tests are valid and that there are two separate implementations that pass them. This step is only necessary if a conformance suite is required (i.e. if there are specific semantics associated with the entry that require software validation)
- If the submission affects the semantic processing of either taxonomies or instances the DTRAM calls for two implementations in the same way as a "Call for Implementations" is made according to [TECH-WG-PROCESSES]. This stage may be bypassed at the discretion of the DTRAM if it is known that two implementations already exist or if semantic processing is not affected.
- A minimum of 30 days of public review follow.
- If a "Call for Implementations" has been issued this step MUST NOT begin until two such implementations are known to the DTRAM. The DTRAM or, if they decide to delegate this step, the referee makes any necessary amendments pursuant to the CR feedback and, unless it determines that a new CR is necessary, the DTRAM recommends to the XSB that it be published as a RECOMMENDATION.
- The XSB approves the RECOMMENDATION and the status of the entry in the DTR is changed to "REC".
 |
The process by which an entry may be updated in the DTR is analogous. If errata are discovered in any data types with "REC" status then a new version of the data type will be entered into the registry following the same process as that used for errata corrections to the specification itself. The effective date of the errata corrected version will be later than that of the original and will thus supersede it.
2.3 Withdrawing a Data Type
Unless a data type has the status of "REC" it may be withdrawn from the DTR at any time upon request of the original submitter. Such request MUST be made to the DTRAM by e-mail to the address published at http://www.xbrl.org/dtr.
A data type with the status "REC" MAY NOT be withdrawn in this manner but MUST follow the process in Section 2.4 for rescinding a RECOMMENDED data type.
2.4 Rescinding a RECOMMENDED Data Type
The process of rescinding a data type is not defined. If a situation arises whereby it becomes necessary to do so it will be defined following the model of [TECH-WG-PROCESSES].